Automotive PCBs are the circuit boards used in automotive electronics from engine controls, anti-lock brake systems, GPS, to rearview cameras and front lights. Safety is the most important consideration for automotive PCB design and manufacturing.
As more and more electric cars and hybrid electric vehicles drive on roads, the demands for reliable automotive PCBs rise.
Automotive PCBs have strict quality requirements and their quality should be traceable. From the first process to the end, the entire manufacturing process of every automotive PCB board is recorded in a "PPAP level 3 required" report, including manufacturing specifications, operators, machine specifications, all features of the board.
The "PPAP level 3 required" report and a COC report (Continuum of Care) are delivered with the automotive PCBs to the buyer.
Automotive PCBs and Applications
Automotive PCBs are used on different occasions in the automotive industry and they are various. The main automotive PCBs and applications are listed below.

Ceramic automotive PCB: ceramic-substrate circuit boards, and usually the ceramic core is aluminum nitride or alumina. Their dominant features are excellent thermal conductivity and high-temperature resistance.
Applications: automotive sensors, engine controls, engine compartment, anti-lock brake controls, power control units, vehicle shock absorbers, turbochargers, automotive LED headlights, motor driver modules, current conversion modules, DC/AC power converters, and IGBT power modules of electrical cars' inverters
HDI automotive PCB: high wiring density circuit boards with blind/buried microvias. The minimum track/space of HDI PCBs used in the automotive industry should be 75μm/75μm or smaller.
Applications: in-vehicle computers, audio-video systems, in-vehicle communication systems
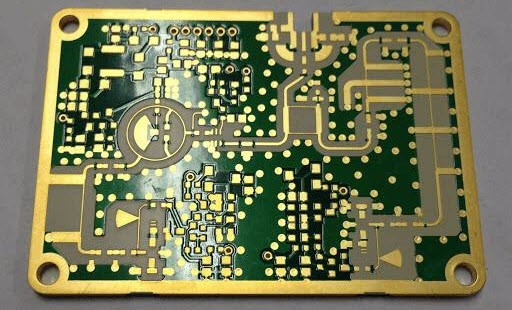
High-frequency automotive PCB: PTFE or hybrid-ceramic printed circuit boards perform as high-frequency wave transmitters and receivers to locate subjects. The signal waves can be high-speed, microwave, radio-frequency waves.
Applications: parking distance controls, forward collision warning systems, vehicular communication systems, automotive navigation systems
Flexible automotive PCB: FPCs are foldable and twistable, and automotive FPCs replacing harnesses has become a trend. It is estimated that a car will use more than 100 automotive flexible PCBs.
Applications: battery management systems, vehicle display modules, vehicle sensors, car lights, vehicle seat sensors, ABS pressure sensors, door handles, gearboxes, roof switches
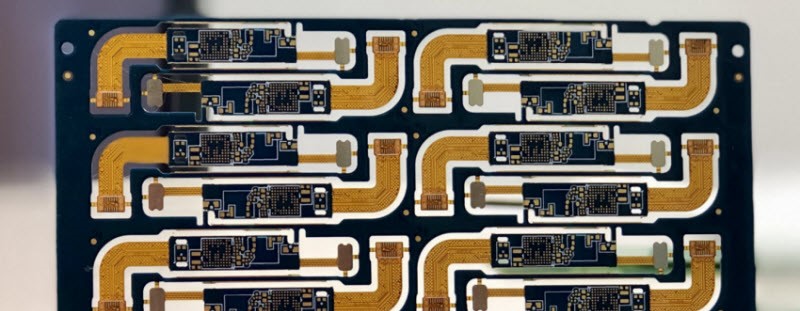
Rigid-flex automotive PCB: rigid-flex PCBs have the advantages of rigid and flexible PCBs. Over the past twenty years, rigid-flex PCBs have been applied by most vehicles to reduce solder joints and connectors.
Applications: vehicle sensors, engine controls, power transmission controls, stability control systems, cameras, navigation controls, gear switches, airbag controls, digital displays
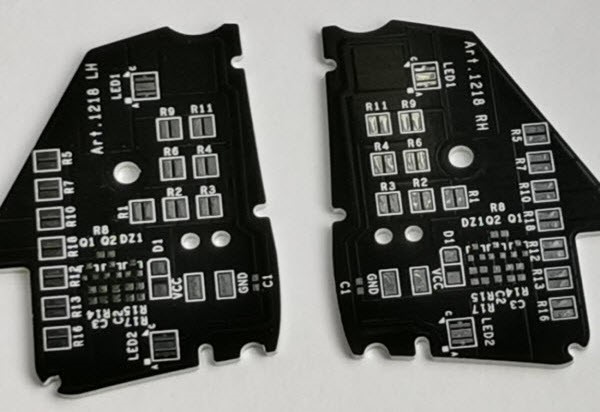
Metal substrate automotive PCB: aluminum or copper-based printed circuit boards. Metal substrate PCBs have better thermal conductivity than FR4 PCBs.
Applications: automotive LED headlights, brake lights, indicator lights
Automotive PCB standards
There are thousands of automotive electronics standards to make sure the safety of drivers and passengers. Automotive PCBs used in different parts of a vehicle have different reliability requirements and have to follow different standards. Below we list the key automotive PCB standards to help R&D engineers to follow the industry requirements.
Standard | Description | Published date | Organization |
AEC-Q100 Rev-H | Describes failure mechanism based stress test qualification for integrated circuits | 11/09/2014 | AEC Component Technical Committee |
AEC - Q101 Rev-E | Prescribes failure mechanism based stress test qualification for discrete semiconductors | 01/03/2021 | AEC Component Technical Committee |
AEC - Q102 Rev-A | Describes failure mechanism based stress test qualification for discrete optoelectronic semiconductors in automotive applications | 06/04/2020 | AEC Component Technical Committee |
AEC - Q103-002 Rev- (Initial Release) | Describes failure mechanism based stress test qualification for micro electro-mechanial system pressure sensor devices | 01/03/2019 | AEC Component Technical Committee |
AEC - Q104 Rev - (Initial Release) | Describes failure mechanism based stress test qualification for multichip modules in automotive applications | 14/09/2017 | AEC Component Technical Committee |
AEC - Q200 Rev-D base | Describes stress test qualification for passive components | 01/06/2010 | AEC Component Technical Committee |
IPC-A-6012DA | Describes requirements for the qualification and performance of rigid printed circuit boards | 01/04/2016 | Association Connecting Electronics Industries |
IPC-6012DA-WAM1 | (Addendum to IPC-6012D) Defines qualification and performance specification for rigid printed boards | 01/12/2018 | Association Connecting Electronics Industries |
IPC-9797 | Describes press-fit standards for printed boards for automotive requirements and other high-reliability applications | 01/06/2020 | Association Connecting Electronics Industries |
IATF 1649:2016 | Defines guidelines and requirements for automotive quality management system | October 2016 | International Automotive Task Force |
The above standards are not comprehensive, but you can use them as basics for your automotive PCB design.


 whatsapp
whatsapp